/*
* Geotools 2 - OpenSource mapping toolkit
* (C) 2003, Geotools Project Managment Committee (PMC)
* (C) 2001, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement
*
* This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with this library; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA
*
*
* This package contains formulas and documentation from the
* National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration. NOAA's work
* is fully acknowledged here.
*/
package org.geotools.nature;
// J2SE dependencies
import java.awt.geom.Point2D;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.TimeZone;
/**
* Calcule la position du soleil relativement à la position de l'observateur.
* Cette classe reçoit en entrés les coordonnées spatio-temporelles de
* l'observateur, soit:
*
*
*
*
* - La longitude (en degrées) de l'observateur;
* - La latitude (en degrées) de l'observateur;
* - La date et heure en heure universelle (GMT).
*
*
* La position du soleil calculée en sortie comprend les valeurs suivantes:
*
*
* - L'azimuth du soleil (en degrés dans le sens des aiguilles d'une montre depuis le nord);
* - L'élévation du soleil (en degrés par rapport a l'horizon).
*
* |
*
*  |
*
*
* Les algorithmes utilisés dans cette classe sont des adaptations des algorithmes
* en javascript écrit par le "National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration,
* Surface Radiation Research Branch". L'application original est le
*
* Solar Position Calculator.
*
*
* The approximations used in these programs are very good for years between
* 1800 and 2100. Results should still be sufficiently accurate for the range
* from -1000 to 3000. Outside of this range, results will be given, but the
* potential for error is higher.
*
* @since 2.1
* @source $URL$
* @version $Id$
* @author Remi Eve
* @author Martin Desruisseaux
*/
public class SunRelativePosition {
/**
* Number of milliseconds in a day.
*/
private static final int DAY_MILLIS = 24*60*60*1000;
/**
* Valeur affectée lorsque un resultat n'est pas calculable du
* fait de la nuit. Cette valeur concerne les valeurs de sorties
* {@link #elevation} et {@link #azimuth}.
*/
private static final double DARK = Double.NaN;
/**
* {@linkplain #getElevation Elevation angle} of astronomical twilight, in degrees.
* Astronomical twilight is the time of morning or evening when the sun is 18° below
* the horizon (solar elevation angle of -18°).
*/
public static final double ASTRONOMICAL_TWILIGHT = -18;
/**
* {@linkplain #getElevation Elevation angle} of nautical twilight, in degrees.
* Nautical twilight is the time of morning or evening when the sun is 12° below
* the horizon (solar elevation angle of -12°).
*/
public static final double NAUTICAL_TWILIGHT = -12;
/**
* {@linkplain #getElevation Elevation angle} of civil twilight, in degrees. Civil
* twilight is the time of morning or evening when the sun is 6° below the horizon
* (solar elevation angle of -6°).
*/
public static final double CIVIL_TWILIGHT = -6;
/**
* Sun's {@linkplain #getElevation elevation angle} at twilight, in degrees.
* Common values are defined for the
* {@linkplain #ASTRONOMICAL_TWILIGHT astronomical twilight} (-18°),
* {@linkplain #NAUTICAL_TWILIGHT nautical twilight} (-12°) and
* {@linkplain #CIVIL_TWILIGHT civil twilight} (-6°).
* If no twilight are defined, then this value is {@linkplain Double#NaN NaN}.
* The {@linkplain #getElevation elevation} and {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth} are
* set to {@linkplain Double#NaN NaN} when the sun elevation is below the twilight
* value (i.e. during night). The default value is {@link #CIVIL_TWILIGHT}.
*/
private double twilight = CIVIL_TWILIGHT;
/**
* Heure à laquelle le soleil est au plus haut dans la journée en millisecondes
* écoulées depuis le 1er janvier 1970.
*/
private long noonTime;
/**
* Azimuth du soleil, en degrés dans le sens des
* aiguilles d'une montre depuis le nord.
*/
private double azimuth;
/**
* Elévation du soleil, en degrés par rapport a l'horizon.
*/
private double elevation;
/**
* Geographic coordinate where current elevation and azimuth were computed.
* Value are in degrees of longitude or latitude.
*/
private double latitude, longitude;
/**
* Date and time when the current elevation and azimuth were computed.
* Value is in milliseconds ellapsed since midnight UTC, January 1st, 1970.
*/
private long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
/**
* {@code true} is the elevation and azimuth are computed, or {@code false}
* if they need to be computed. This flag is set to {@code false} when the date
* and/or the coordinate change.
*/
private boolean updated;
/**
* Calculate the equation of center for the sun. This value is a correction
* to add to the geometric mean longitude in order to get the "true" longitude
* of the sun.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Equation of center in degrees.
*/
private static double sunEquationOfCenter(final double t) {
final double m = Math.toRadians(sunGeometricMeanAnomaly(t));
return Math.sin(1*m) * (1.914602 - t*(0.004817 + 0.000014*t)) +
Math.sin(2*m) * (0.019993 - t*(0.000101 )) +
Math.sin(3*m) * (0.000289);
}
/**
* Calculate the Geometric Mean Longitude of the Sun.
* This value is close to 0° at the spring equinox,
* 90° at the summer solstice, 180° at the automne equinox
* and 270° at the winter solstice.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Geometric Mean Longitude of the Sun in degrees,
* in the range 0° (inclusive) to 360° (exclusive).
*/
private static double sunGeometricMeanLongitude(final double t) {
double L0 = 280.46646 + t*(36000.76983 + 0.0003032*t);
L0 = L0 - 360*Math.floor(L0/360);
return L0;
}
/**
* Calculate the true longitude of the sun. This the geometric mean
* longitude plus a correction factor ("equation of center" for the
* sun).
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun's true longitude in degrees.
*/
private static double sunTrueLongitude(final double t) {
return sunGeometricMeanLongitude(t) + sunEquationOfCenter(t);
}
/**
* Calculate the apparent longitude of the sun.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun's apparent longitude in degrees.
*/
private static double sunApparentLongitude(final double t) {
final double omega = Math.toRadians(125.04 - 1934.136 * t);
return sunTrueLongitude(t) - 0.00569 - 0.00478 * Math.sin(omega);
}
/**
* Calculate the Geometric Mean Anomaly of the Sun.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Geometric Mean Anomaly of the Sun in degrees.
*/
private static double sunGeometricMeanAnomaly(final double t) {
return 357.52911 + t * (35999.05029 - 0.0001537*t);
}
/**
* Calculate the true anamoly of the sun.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun's true anamoly in degrees.
*/
private static double sunTrueAnomaly(final double t) {
return sunGeometricMeanAnomaly(t) + sunEquationOfCenter(t);
}
/**
* Calculate the eccentricity of earth's orbit. This is the ratio
* {@code (a-b)/a} where a is the semi-major axis
* length and b is the semi-minor axis length. Value
* is 0 for a circular orbit.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return The unitless eccentricity.
*/
private static double eccentricityEarthOrbit(final double t) {
return 0.016708634 - t*(0.000042037 + 0.0000001267*t);
}
/**
* Calculate the distance to the sun in Astronomical Units (AU).
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun radius vector in AUs.
*/
private static double sunRadiusVector(final double t) {
final double v = Math.toRadians(sunTrueAnomaly(t));
final double e = eccentricityEarthOrbit(t);
return (1.000001018 * (1 - e*e)) / (1 + e*Math.cos(v));
}
/**
* Calculate the mean obliquity of the ecliptic.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Mean obliquity in degrees.
*/
private static double meanObliquityOfEcliptic(final double t) {
final double seconds = 21.448 - t*(46.8150 + t*(0.00059 - t*(0.001813)));
return 23.0 + (26.0 + (seconds/60.0))/60.0;
}
/**
* Calculate the corrected obliquity of the ecliptic.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Corrected obliquity in degrees.
*/
private static double obliquityCorrected(final double t) {
final double e0 = meanObliquityOfEcliptic(t);
final double omega = Math.toRadians(125.04 - 1934.136*t);
return e0 + 0.00256 * Math.cos(omega);
}
/**
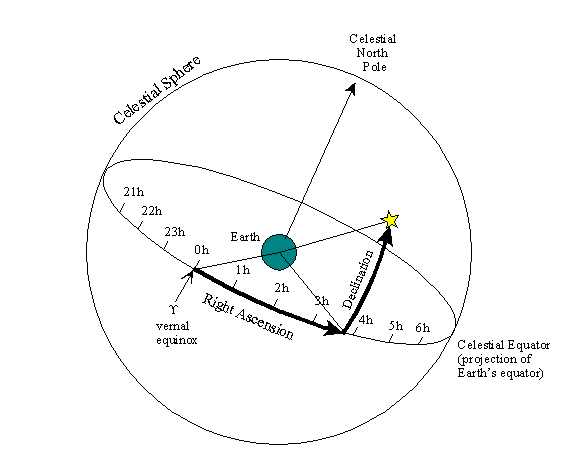
* Calculate the right ascension of the sun. Similar to the angular system
* used to define latitude and longitude on Earth's surface, right ascension
* is roughly analogous to longitude, and defines an angular offset from the
* meridian of the vernal equinox.
*
*

*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun's right ascension in degrees.
*/
private static double sunRightAscension(final double t) {
final double e = Math.toRadians(obliquityCorrected(t));
final double b = Math.toRadians(sunApparentLongitude(t));
final double y = Math.sin(b) * Math.cos(e);
final double x = Math.cos(b);
final double alpha = Math.atan2(y, x);
return Math.toDegrees(alpha);
}
/**
* Calculate the declination of the sun. Declination is analogous to latitude
* on Earth's surface, and measures an angular displacement north or south
* from the projection of Earth's equator on the celestial sphere to the
* location of a celestial body.
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Sun's declination in degrees.
*/
private static double sunDeclination(final double t) {
final double e = Math.toRadians(obliquityCorrected(t));
final double b = Math.toRadians(sunApparentLongitude(t));
final double sint = Math.sin(e) * Math.sin(b);
final double theta = Math.asin(sint);
return Math.toDegrees(theta);
}
/**
* Calculate the Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) of solar noon for the given day
* at the given location on earth.
*
* @param lon longitude of observer in degrees.
* @param eqTime Equation of time.
* @return Time in minutes from beginnning of day in UTC.
*/
private static double solarNoonTime(final double lon, final double eqTime) {
return 720.0 + (lon * 4.0) - eqTime;
}
/**
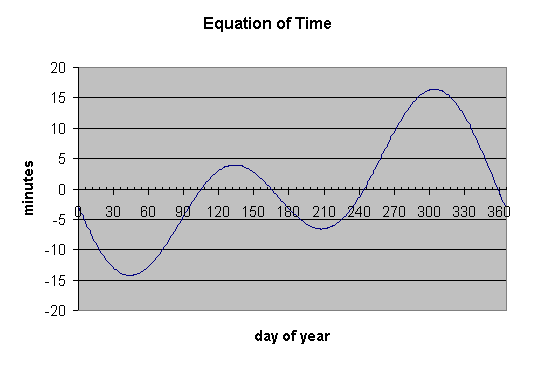
* Calculate the difference between true solar time and mean. The "equation
* of time" is a term accounting for changes in the time of solar noon for
* a given location over the course of a year. Earth's elliptical orbit and
* Kepler's law of equal areas in equal times are the culprits behind this
* phenomenon. See the
* Analemma page.
* Below is a plot of the equation of time versus the day of the year.
*
* 
*
* @param t number of Julian centuries since J2000.
* @return Equation of time in minutes of time.
*/
private static double equationOfTime(final double t) {
double eps = Math.toRadians(obliquityCorrected(t));
double l0 = Math.toRadians(sunGeometricMeanLongitude(t));
double m = Math.toRadians(sunGeometricMeanAnomaly(t));
double e = eccentricityEarthOrbit(t);
double y = Math.tan(eps/2);
y *= y;
double sin2l0 = Math.sin(2 * l0);
double cos2l0 = Math.cos(2 * l0);
double sin4l0 = Math.sin(4 * l0);
double sin1m = Math.sin(m);
double sin2m = Math.sin(2 * m);
double etime = y*sin2l0 - 2*e*sin1m + 4*e*y*sin1m*cos2l0
- 0.5*y*y*sin4l0 - 1.25*e*e*sin2m;
return Math.toDegrees(etime)*4.0;
}
/**
* Computes the refraction correction angle.
* The effects of the atmosphere vary with atmospheric pressure, humidity
* and other variables. Therefore the calculation is approximate. Errors
* can be expected to increase the further away you are from the equator,
* because the sun rises and sets at a very shallow angle. Small variations
* in the atmosphere can have a larger effect.
*
* @param zenith The sun zenith angle in degrees.
* @return The refraction correction in degrees.
*/
private static double refractionCorrection(final double zenith) {
final double exoatmElevation = 90 - zenith;
if (exoatmElevation > 85) {
return 0;
}
final double refractionCorrection; // In minute of degrees
final double te = Math.tan(Math.toRadians(exoatmElevation));
if (exoatmElevation > 5.0) {
refractionCorrection = 58.1/te - 0.07/(te*te*te) + 0.000086/(te*te*te*te*te);
} else {
if (exoatmElevation > -0.575) {
refractionCorrection = 1735.0 + exoatmElevation *
(-518.2 + exoatmElevation *
( 103.4 + exoatmElevation *
(-12.79 + exoatmElevation *
0.711)));
} else {
refractionCorrection = -20.774 / te;
}
}
return refractionCorrection / 3600;
}
/**
* Constructs a sun relative position calculator.
*/
public SunRelativePosition() {
}
/**
* Constructs a sun relative position calculator with the specified value
* for the {@linkplain #setTwilight sun elevation at twilight}.
*
* @param twilight The new sun elevation at twilight, or {@link Double#NaN}
* if no twilight value should be taken in account.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the twilight value is illegal.
*/
public SunRelativePosition(final double twilight) throws IllegalArgumentException {
setTwilight(twilight);
}
/**
* Calculates solar position for the current date, time and location.
* Results are reported in azimuth and elevation in degrees.
*/
private void compute() {
double latitude = this.latitude;
double longitude = this.longitude;
// NOAA convention use positive longitude west, and negative east.
// Inverse the sign, in order to be closer to OpenGIS convention.
longitude = -longitude;
// Compute: 1) Julian day (days ellapsed since January 1, 4723 BC at 12:00 GMT).
// 2) Time as the centuries ellapsed since January 1, 2000 at 12:00 GMT.
final double julianDay = Calendar.julianDay(this.time);
final double time = (julianDay-2451545)/36525;
double solarDec = sunDeclination(time);
double eqTime = equationOfTime(time);
this.noonTime = Math.round(solarNoonTime(longitude, eqTime) * (60*1000)) +
(this.time/DAY_MILLIS)*DAY_MILLIS;
// Formula below use longitude in degrees. Steps are:
// 1) Extract the time part of the date, in minutes.
// 2) Apply a correction for longitude and equation of time.
// 3) Clamp in a 24 hours range (24 hours == 1440 minutes).
double trueSolarTime = ((julianDay+0.5) - Math.floor(julianDay+0.5)) * 1440;
trueSolarTime += (eqTime - 4.0*longitude); // Correction in minutes.
trueSolarTime -= 1440*Math.floor(trueSolarTime/1440);
// Convert all angles to radians. From this point until
// the end of this method, local variables are always in
// radians. Output variables ('azimuth' and 'elevation')
// will still computed in degrees.
longitude = Math.toRadians(longitude);
latitude = Math.toRadians(latitude );
solarDec = Math.toRadians(solarDec );
double csz = Math.sin(latitude) *
Math.sin(solarDec) +
Math.cos(latitude) *
Math.cos(solarDec) *
Math.cos(Math.toRadians(trueSolarTime/4 - 180));
if (csz > +1) csz = +1;
if (csz < -1) csz = -1;
final double zenith = Math.acos(csz);
final double azDenom = Math.cos(latitude) * Math.sin(zenith);
//////////////////////////////////////////
//// Compute azimuth in degrees ////
//////////////////////////////////////////
if (Math.abs(azDenom) > 0.001) {
double azRad = ((Math.sin(latitude)*Math.cos(zenith)) - Math.sin(solarDec)) / azDenom;
if (azRad > +1) azRad = +1;
if (azRad < -1) azRad = -1;
azimuth = 180 - Math.toDegrees(Math.acos(azRad));
if (trueSolarTime > 720) { // 720 minutes == 12 hours
azimuth = -azimuth;
}
} else {
azimuth = (latitude>0) ? 180 : 0;
}
azimuth -= 360*Math.floor(azimuth/360);
////////////////////////////////////////////
//// Compute elevation in degrees ////
////////////////////////////////////////////
final double refractionCorrection = refractionCorrection(Math.toDegrees(zenith));
final double solarZen = Math.toDegrees(zenith) - refractionCorrection;
elevation = 90 - solarZen;
if (elevation < twilight) {
// do not report azimuth & elevation after twilight
azimuth = DARK;
elevation = DARK;
}
updated = true;
}
/**
* Set the geographic coordinate where to compute the {@linkplain #getElevation elevation}
* and {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth}.
*
* @param longitude The longitude in degrees. Positive values are East; negative values are West.
* @param latitude The latitude in degrees. Positive values are North, negative values are South.
*/
public void setCoordinate(double longitude, double latitude) {
if (latitude > +89.8) latitude = +89.8;
if (latitude < -89.8) latitude = -89.8;
if (latitude != this.latitude || longitude != this.longitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
this.longitude = longitude;
this.updated = false;
}
}
/**
* Set the geographic coordinate where to compute the {@linkplain #getElevation elevation}
* and {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth}.
*
* @param point The geographic coordinates in degrees of longitude and latitude.
*/
public void setCoordinate(final Point2D point) {
setCoordinate(point.getX(), point.getY());
}
/**
* Returns the coordinate used for {@linkplain #getElevation elevation} and
* {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth} computation. This is the coordinate
* specified during the last call to a {@link #setCoordinate(double,double)
* setCoordinate(...)} method.
*/
public Point2D getCoordinate() {
return new Point2D.Double(longitude, latitude);
}
/**
* Set the date and time when to compute the {@linkplain #getElevation elevation}
* and {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth}.
*
* @param date The date and time.
*/
public void setDate(final Date date) {
final long time = date.getTime();
if (time != this.time) {
this.time = time;
this.updated = false;
}
}
/**
* Returns the date used for {@linkplain #getElevation elevation} and
* {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth} computation. This is the date specified
* during the last call to {@link #setDate}.
*/
public Date getDate() {
return new Date(time);
}
/**
* Set the sun's {@linkplain #getElevation elevation angle} at twilight, in degrees.
* Common values are defined for the
* {@linkplain #ASTRONOMICAL_TWILIGHT astronomical twilight} (-18°),
* {@linkplain #NAUTICAL_TWILIGHT nautical twilight} (-12°) and
* {@linkplain #CIVIL_TWILIGHT civil twilight} (-6°).
* The {@linkplain #getElevation elevation} and {@linkplain #getAzimuth azimuth} are
* set to {@linkplain Double#NaN NaN} when the sun elevation is below the twilight
* value (i.e. during night). The default value is {@link #CIVIL_TWILIGHT}.
*
* @param twilight The new sun elevation at twilight, or {@link Double#NaN}
* if no twilight value should be taken in account.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the twilight value is illegal.
*/
public void setTwilight(final double twilight) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (twilight<-90 || twilight>-90) {
// TODO: provides a better (localized) message.
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.valueOf(twilight));
}
this.twilight = twilight;
this.updated = false;
}
/**
* Returns the sun's {@linkplain #getElevation elevation angle} at twilight, in degrees.
* This is the value set during the last call to {@link #setTwilight}.
*/
public double getTwilight() {
return twilight;
}
/**
* Retourne l'azimuth en degrés.
*
* @return L'azimuth en degrés.
*/
public double getAzimuth() {
if (!updated) {
compute();
}
return azimuth;
}
/**
* Retourne l'élévation en degrés.
*
* @return L'élévation en degrés.
*/
public double getElevation() {
if (!updated) {
compute();
}
return elevation;
}
/**
* Retourne l'heure à laquelle le soleil est au plus haut. L'heure est
* retournée en nombre de millisecondes écoulées depuis le debut de la
* journée (minuit) en heure UTC.
*/
public long getNoonTime() {
if (!updated) {
compute();
}
return noonTime % DAY_MILLIS;
}
/**
* Retourne la date à laquelle le soleil est au plus haut dans la journée.
* Cette méthode est équivalente à {@link #getNoonTime} mais inclue le jour
* de la date qui avait été spécifiée à la méthode {@link #compute}.
*/
public Date getNoonDate() {
if (!updated) {
compute();
}
return new Date(noonTime);
}
/**
* Affiche la position du soleil à la date et coordonnées spécifiée.
* Cette application peut être lancée avec la syntaxe suivante:
*
* SunRelativePosition [longitude] [latitude] [date]
*
* où date est un argument optionel spécifiant la date et l'heure.
* Si cet argument est omis, la date et heure actuelles seront utilisées.
*/
public static void main(final String[] args) throws ParseException {
final DateFormat format=DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.SHORT, DateFormat.SHORT);
format.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
double longitude = 0;
double latitude = 0;
Date time = new Date();
switch (args.length) {
case 3: time = format.parse (args[2]); // fall through
case 2: latitude = Double.parseDouble(args[1]); // fall through
case 1: longitude = Double.parseDouble(args[0]); // fall through
}
final SunRelativePosition calculator = new SunRelativePosition();
calculator.setDate(time);
calculator.setCoordinate(longitude, latitude);
System.out.print("Date (UTC): "); System.out.println(format.format(time));
System.out.print("Longitude: "); System.out.println(longitude);
System.out.print("Latitude: "); System.out.println(latitude);
System.out.print("Elevation: "); System.out.println(calculator.getElevation());
System.out.print("Azimuth: "); System.out.println(calculator.getAzimuth());
System.out.print("Noon date: "); System.out.println(format.format(calculator.getNoonDate()));
}
}

