DESCRIPTION
v.kernel generates a raster density map from vector points
data using a moving
kernel. Available kernel
density functions are uniform, triangular, epanechnikov,
quartic, triweight, gaussian, cosine, default
is gaussian.
The module can also generate a vector density map on a vector network.
Conventional kernel functions produce biased estimates by overestimating
the densities around network nodes, whereas the equal split method of
Okabe et al. (2009) produces unbiased density estimates. The equal split
method uses the kernel function selected with the kernel option
and can be enabled with node=split.
NOTES
The multiplier option is needed to overcome the limitation that
the resulting density in case of a vector map output is stored as category
(integer). The density result stored as category may be multiplied by this number.
For the gaussian kernel, standard deviation for the
gaussian function
is set to 1/4 of the radius.
With the -o flag (experimental) the command tries to calculate an
optimal radius. The value of radius is taken
as maximum value. The radius is calculated based on the gaussian function,
using ALL points, not just those in the current region.
EXAMPLES
Compute density of points (using vector map of schools from North Carolina sample dataset):
g.region region=wake_30m
v.kernel input=schools_wake output=schools_density radius=5000 multiplier=1000000
r.colors map=schools_density color=bcyr
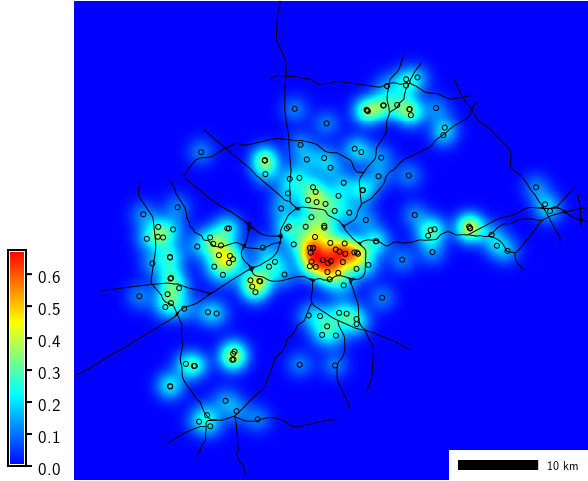
School density
KNOWN ISSUES
The module only considers the presence of points, but not
(yet) any attribute values.
REFERENCES
- Okabe, A., Satoh, T., Sugihara, K. (2009). A kernel density estimation
method for networks, its computational method and a GIS-based tool.
International Journal of Geographical Information Science, Vol 23(1),
pp. 7-32.
DOI: 10.1080/13658810802475491
SEE ALSO
v.surf.rst
Overview: Interpolation and Resampling in GRASS GIS
AUTHORS
Stefano Menegon, ITC-irst, Trento, Italy
Radim Blazek (additional kernel density functions and network part)
Last changed: $Date$

