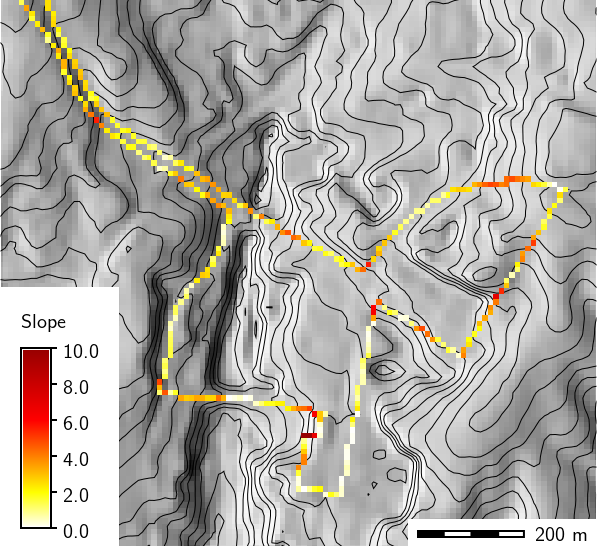
Slope in degrees along bus route
v.to.rast will only affect data in areas lying inside the boundaries of the current geographic region. A grid cell belongs to the area where the grid cell center falls into.
Before running v.to.rast, the user should therefore ensure that the current geographic region is correctly set and that the region resolution is at the desired level.
Either the column parameter or the value parameter must be specified. The use option may be specified alone when using the dir option.
use options are:
The column parameter uses an existing column from the vector map database table as the category value in the output raster map. Existing table columns can be shown by using db.describe.
An empty raster map layer will be created if the vector map layer has not been assigned category/attribute labels (e.g., through use of v.category option=add).
Otherwise:
Line directions are given in degrees counterclockwise from east.
Raster category labels are supported for all of use= except use=z.
The -d flag applies only to lines and boundaries, the default is to set only those cells on the render path (thin line).
Boundaries (usually without categories) can be rasterized with
v.to.rast type=boundary layer=-1 use=val
db.describe -c table=vect_map ncols:3 Column 1: CAT Column 2: SPEED Column 3: WIDTH
v.to.rast input=vect_map output=raster_map attribute_column=SPEED type=line
v.to.rast input=streams output=streamsdir use=dir
g.region raster=elevation -p r.slope.aspect elevation=elevation slope=slope aspect=aspect # compute direction of the bus route v.to.rast input=busroute11 type=line output=busroute11_dir use=dir # extract steepest slope values and transform them into slope along path r.mapcalc "route_slope = if(busroute11, slope)" r.mapcalc "route_slope_dir = abs(atan(tan(slope) * cos(aspect - busroute11_dir)))"

v.to.rast input=fields output=myfields use=attr attribute_column=cat label_column=label r.category myfields
g.copy vector=schools_wake,myschools_wake
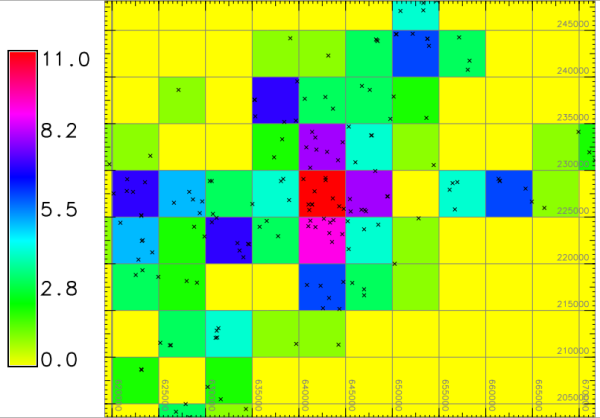
# set computation region for raster binning
g.region vector=myschools_wake res=5000 -p -a
# add new column for counting
v.db.addcolumn myschools_wake column="value integer"
v.db.update myschools_wake column=value value=1
# verify attributes
v.db.select myschools_wake column=cat,value
v.out.ascii input=myschools_wake output=- column=value
# export and import on the fly, use 4th column (value) as input
v.out.ascii input=myschools_wake output=- column=value | r.in.xyz input=- \
z=4 output=schools_wake_aggreg method=sum
d.mon wx0
d.rast schools_wake_aggreg
d.vect schools_wake
d.grid 5000
Last changed: $Date$